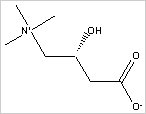
| WHAT IS L-CARNITINE? | |
L-Carnitine is an amino acid derivative found in nearly all cells of the body but in especially high concentrations in human heart and liver tissue. L-Carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane within the mitochondria, where they are processed by beta-oxidation into energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). L-Carnitine works synergistically with Co-Q10, an antioxidant and energy co-factor that is found in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. L-Carnitine, also called levocarnitine, is an essential component of foods of animal origin occurring naturally in meat and meat extracts. L-Carnitine is a vitamin-like nutrient, related to B vitamins and was once called Vitamin BT. L-Carnitine is a physiological substance, essential for energy production and for fat metabolism. L-Carnitine can be synthesized in the human liver, but insufficient amounts are produced in infants, in adolescents and in adults under certain physiological conditions.
|
|
|
|
| BACK TO SLIM EDGE |